Marie Antoinette story
Marie Antoinette story
Did the woman who supposely said “let them eat cake” get her just desserts ?
During her lifetime, the extravagant queen was dubbed “Mrs. Deficit”, the “Austrian Bitch” and even worse... Many slurs still linger to date. Wasn’t she the queen who said “Let them eat cake” when she heard the people were starving in Paris?
Sofia Coppola’s latest film elegantly addresses these issues and attempts to restore the image of a young girl who grew to maturity in a court mired in political intrigue and oppressive etiquette for which she was ill-prepared
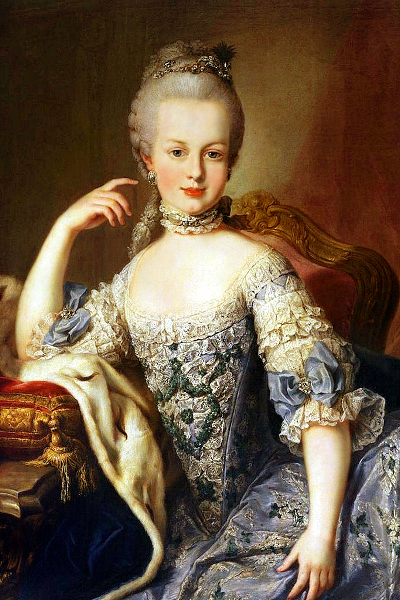

in her young days
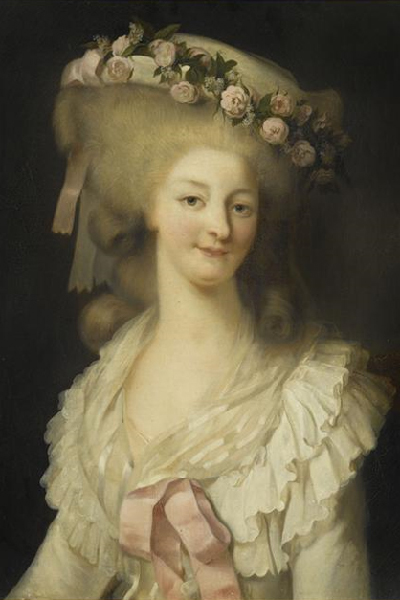


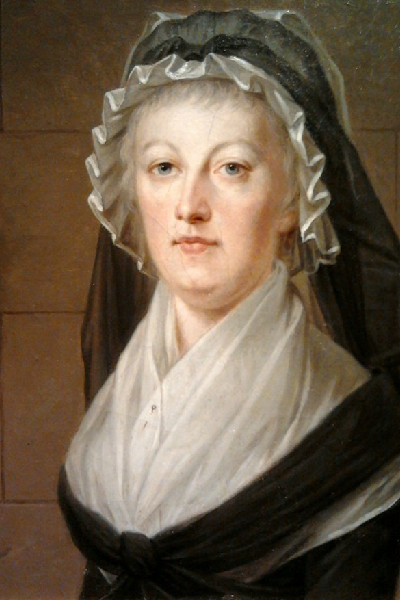
Marie Antoinette's best friend
At first, Marie-Antoinette was beloved by the people of France as the embodiment of youth, beauty and promise... She gave generously to those in need. But, at court, factions were forming.
Tongues were wagging. Was her husband, Louis XVI impotent? Marie-Antoinette must be getting satisfaction elsewhere... from the king’s handsome younger brother... from her good friend Princess Lamballe, newly appointed Mistress of the Wardrobe, and later Madame Polignac, governess to her children (when she did finally produce them).
Irritated by the crushing court etiquette, Antoinette dismissed those whose positions had been a closely guarded privilege, and instead selected friends who amused her. As a result, enemies were piling up.
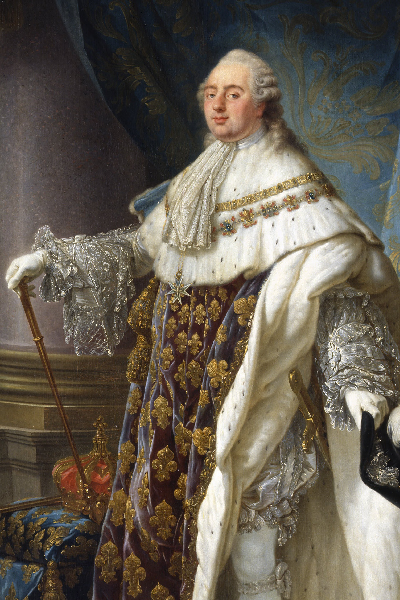
Louis, a bit of a slouch, wasn’t all that popular either. His cousin, Philippe d’Orléans, had his eye on the throne. So did Louis’ younger brothers... And they were all happy to criticize him, the indecisive fool, and his wife, the spendthrift shrew. They fueled demonizing broadsheets in Paris and printed some of their own.
These damning newspapers and pamphlets appeared with increasing frequency and virulence as the revolution was about to explode! By 1785, the once-beloved Antoinette was known as the “Autrichienne” (the Austrian bitch) after she pushed her influence on Louis to help her brother, the Archduke in a political fracas in Poland. Louis didn’t come to Austria’s aid, but the fear was there. Antoinette’s ulterior allegiance must be to her native country.
State bankruptcy was looming in France. The broadsheets printed stories of Antoinette’s huge expenses, inciting the new epithet “Mrs. Deficit”. Her expenditures were a concern and definitely over-the-top. The same could be said of Louis XIV’s mistress, Madame de Montespan and Louis XV’s mistress, Madame du Barry. However, nobody printed their extravagances...
Then came the fluke hail storm and crop failure of 1788. Already detested, mistrusted and dragged through the media mud, another smear came into print. The heartless queen was reported to have said, if there was no bread to be had, then the people should eat brioche (cake). She never said it, but people believed it. Her detractors took advantage of the suffering to fabricate another smear about her in the press. And it’s still taught in history books today – 2 centuries later – a testament to the power of the press in its burgeoning days.
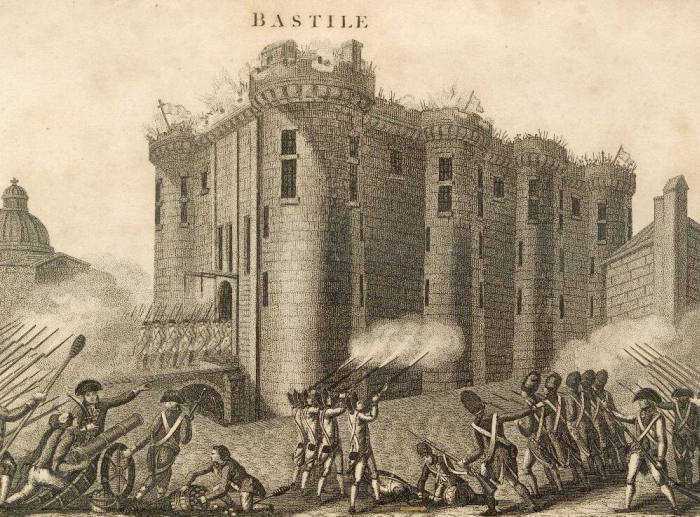

The former Bastille Castle, demolished in 1789
After the Bastille fell in July 1789, and the revolution had begun in earnest with the battle cry: “liberty, equality and fraternity”, people were still starving. The women of Paris, disgusted and spurred by agitators and the press once again, marched to Versailles on October 5, 1789 to return the royal family to Paris (the crowds sarcastically called them the baker, the baker’s wife and the little crumbs)... And this is where Sofia Coppola’s film ends.
Her movie spares us the royals’ steady descent into hell. Taken to the Tuileries Palace (a section of the Louvres that was burned down in 1871), life went on for the family almost as it did in Versailles. But they were closely guarded. Their only hope was to flee France. In 1791, they did, but it was a botched attempt. Spotted and caught in Varennes, not far from the Belgian border, they were returned to Paris. The bungled escape probably sounded the death knell of royalty in France. Any idea of a limited monarchy, like in England, was squelched. Within days of their humiliating return, Marie-Antoinette’s hair went completely white – at age 35!
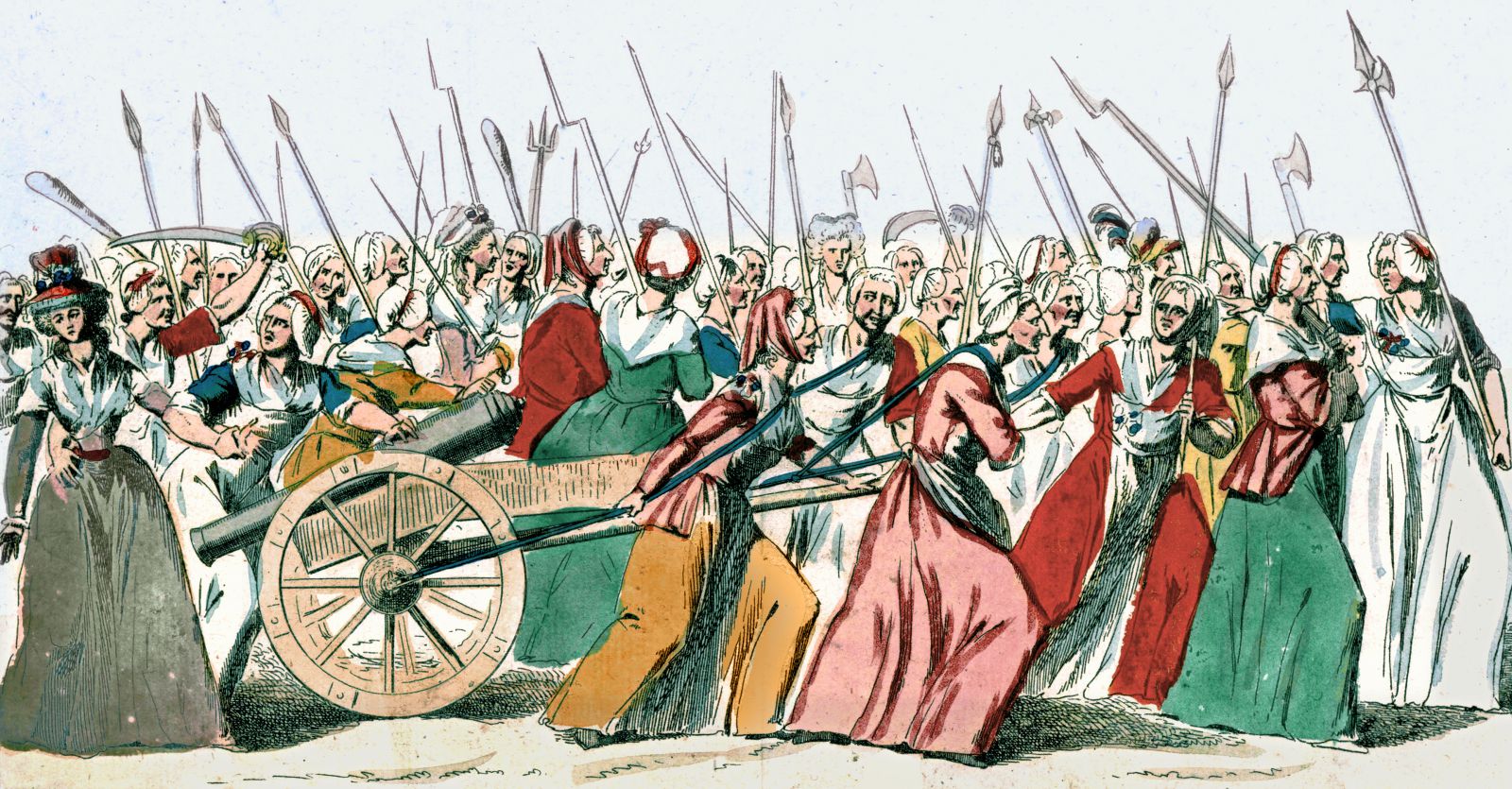

The Parisians starving and protesting on the way to Versailles
Things went from bad to worse. War against France’s invading enemies, Austria and Germany, was going badly. On two occasions, the Tuileries Palace was invaded by the Paris mob. June 20, 1792, the king faced the marauding crowds and managed to calm them. It was only temporary. More defeats on the front stirred up the people and on August 10, 1792, the Parisians attacked again.
To avoid being torn to shreds, the royal family made their way to the legal body nearby, the Assembly, for protection. They escaped a massacre that would have surely finished them off. According to the reports, it was a ghoulish event. People played kickball with the severed heads of the Swiss Guard and worse.
The Assembly eventually voted to abolish the monarchy and the family was taken to a prison in the Marais on August 13, 1792. The prison, known as the Temple, was a medieval remnant that had belonged to the Knights Templar. These were the last poignant months the royals remained together as a family.
.jpg) A defeat at Verdun on September 2, 1792 created another backlash in Paris. An estimated 1,200 people were taken from prisons and butchered. Killed in any way the crowd chose, they were shot, burned alive, hacked to bits, torn to shreds... One unfortunate victim was Princess Lamballe, Marie-Antoinette’s close friend. Incarcerated at La Force, a prison on rue Pavée in the Marais (later destroyed to extend the street), she came to a brutal end. When she defended her friend, the Queen, she was stripped, raped, torn from limb to limb... Her head and genitals were placed on a pike and paraded beneath the Temple window, about 2 miles up the road, and her leg was shot from a cannon. Marie-Antoinette must have trembled when the remains were paraded beneath her prison window.
A defeat at Verdun on September 2, 1792 created another backlash in Paris. An estimated 1,200 people were taken from prisons and butchered. Killed in any way the crowd chose, they were shot, burned alive, hacked to bits, torn to shreds... One unfortunate victim was Princess Lamballe, Marie-Antoinette’s close friend. Incarcerated at La Force, a prison on rue Pavée in the Marais (later destroyed to extend the street), she came to a brutal end. When she defended her friend, the Queen, she was stripped, raped, torn from limb to limb... Her head and genitals were placed on a pike and paraded beneath the Temple window, about 2 miles up the road, and her leg was shot from a cannon. Marie-Antoinette must have trembled when the remains were paraded beneath her prison window.
La Conciergerie, dernière demeure de Marie-Antoinette
It was devastating for the family left in the tower. And things got grimmer still when the order came to separate young Louis (the royalists deemed him Louis XVII), from his mother on July 13, 1793. It was an agony she could not bear and the arguing went on for some time before the little boy was finally torn from his mother’s arms.
He was placed under the care of the illiterate Citizen Richard, a vulgar cobbler, who was told to re-educate the royal child. The little 8-year-old was naturally impressionable and vulnerable after the forced separation. Young Louis was taught revolutionary songs and learned to curse his mother, just upstairs.
Then came the order for Marie-Antoinette’s transfer to la Conciergerie on August 2, 1793. She wasn’t questioned until October 12 as her accusers tried to assemble conclusive evidence against her.
When the questioning did come, she answered with dignity and incredible intelligence:
“Do you think Kings are necessary for a people’s happiness”?
“An individual cannot make such a decision.”
“You must certainly regret your son’s loss of the throne which the people, finally aware of their rights, have destroyed?”
“I shall regret nothing for my son when his country is happy.”
Her answers were incisive and irreproachable.
Then her old arch-enemy launched an attack that took her by surprise.
Hébert, the radical editor of the debauched and racy newpaper “Le Pere Duchêne”, the man who coined “l’Autrichienne”, accused her of incest with her son. Her only response was to look away silently. Surprised by her reaction, a juror pressed her for a response:
“Nature itself shudders at such an accusation made to a mother... I appeal to all mothers here!” Compassion for this frail woman filled the room. Even the vindictive tricoteuses (knitters) who sat through all the trials and executions, had pity for her.
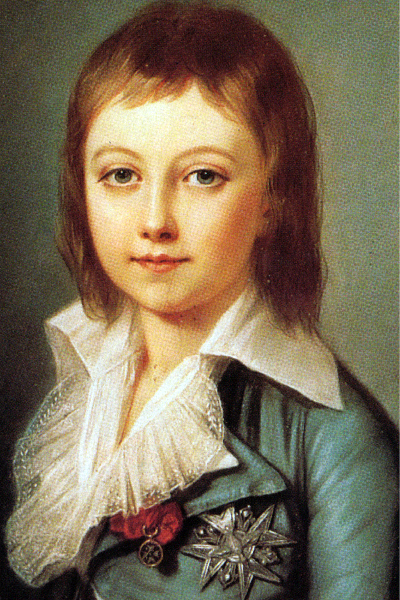
of 6, only 3 portraits of him
were made.

Temple Dungeon

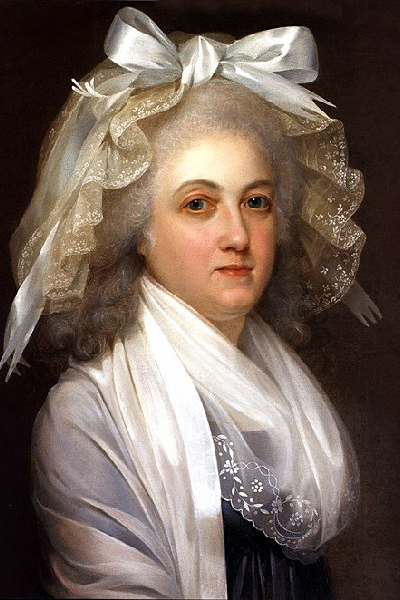
in her last days
But it was a foregone conclusion: “guilty of treason as charged.” Later that day, she was collected in a tumbril, an open wooden cart used for all commoners. Louis had been transported in a carriage. The years of stress, riots, violence, murder, execution and separation from her children had taken a toll on her. She was hemmorhaging badly. Antoinette had a moment of weakness before she stepped into the wagon, and relieved her bowels in la Conciergerie courtyard.
The painter Jacques-Louis David captured her wretched ride down rue St. Honoré. Hair cropped by the executioner, her hands tied behind her back, she looks dignified, haggard, stoic, courageous.
Marie-Antoinette went to the guillotine with poise and deportment. During the Terror, many of the revolutionary leaders themselves faced the “national razor”. Her foe, Hébert, went kicking and screaming. When it came time for Fouquier-Tinvilles, her prosecutor, to face the “widow maker”, he claimed he was just doing his job and whimpered, “I’m the axe, you don’t kill the axe!”.
Clearly the Revolution was fraught with excesses and thousands met an untimely end, but somehow in the popular imagination, Marie-Antoinette became the embodiment of all evils. 200 years later, can we cut the girl some slack! Pamela Grant died in 2014, she was a fantastic friend, historian and tour guide. Her writings is the best way to keep alive her memory.
Pamela Grant ✡



.jpg)